Malaysia Productivity Blueprint
Overview
Productivity is the single most important factor in a country’s long-term growth. High-productivity nations are able to quickly adapt to changes in macroeconomic challenges, as well as fundamental shifts brought on by technological advancement. Realising the importance of productivity to the nation, the 11MP has specified unlocking the potential of productivity as one of the 6 game-changers for the country to achieve high-income status by 2020. Productivity has been identified as the most vital part in the 11MP’s implementation, which calls for renewed efforts to boost productivity in a focussed and targeted manner, with clear outcomes at the national, sectoral, and enterprise levels. The 11MP has introduced the Malaysia Productivity Blueprint (MPB) in May2017 as a strategy to realise this aspiration.
The blueprint has been designed and developed to accelerate productivity improvement strategies, initiatives and programmes at the national, sectoral and enterprise levels. It provides guided implementation to expedite productivity improvements as envisaged in the 11MP through five strategic thrusts. These thrusts are to ensure holistic and systematic change rather than fragmented efforts.
In striving for higher productivity growth, Malaysia must prepare for uncertain external factors as shifts in economic policies could affect a diverse range of outcomes for the Malaysian economy and local labour market conditions. Such externalities can be mitigated by stronger collaboration among the stakeholders through the establishment of various productivity nexus.
National-Level
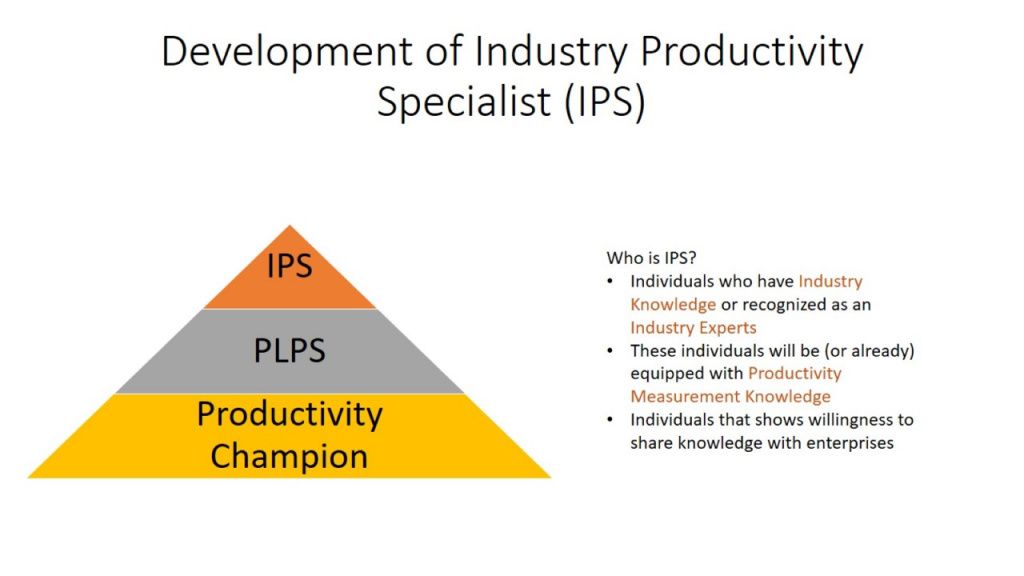
The Blueprint presents a holistic approach towards unlocking the potential of productivity of the nation by addressing productivity challenges at all levels – national, sector and enterprise levels. This new approach to productivity will shift from primarily government-driven initiatives at the national level to targetted actions across industry players and individual enterprises, with industry champions identified to role model change and ensure buy-in across stakeholders.
DRIVING DIGITALISATION AND INNOVATION
Strengthening the readiness of enterprises to effectively adopt and exploit technology and digital advantage (such as 4th industry Revolution).
MAKING INDUSTRY ACCOUNTABLE FOR PRODUCTIVITY
Reducing reliance on non-critical subsidies, linking financial assistance and liberalisation efforts to productivity outcomes, and strengthening industry positioning in higher value add segments of the value chain.
FORGING A ROBUST ECOSYSTEM
Addressing regulatory constraints and developing a robust accountability system to ensure effective implementation of regulatory reviews.

SECURING A STRONG IMPLEMENTATION MECHANISM
Embedding culture of productivity through nationwide movement, and driving accountability in productivity performance through effective governance mechanism.
Sector-Level
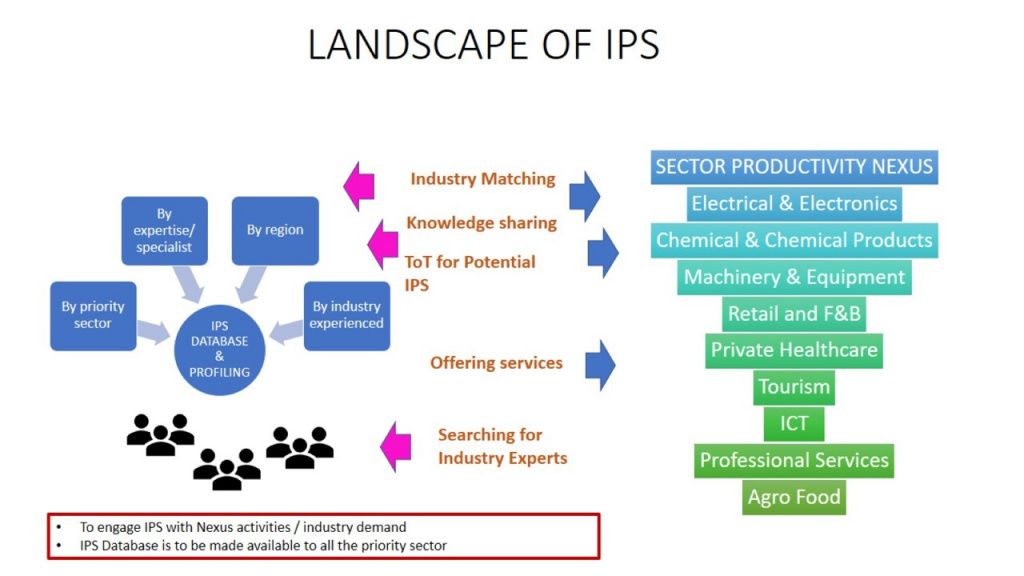
As there is a wide variation in challenges for different sectors and industries, additional sector-specific initiatives are critical for productivity improvement. This chapter outlines the sector-level challenges and initiatives for nine priority subsectors. Sector-specific initiatives are proposed, including the setting up of sector Productivity Nexus to drive the implementation of the initiatives in close partnership with the government.

Digital
Machinery & Equipment
Professional Services

Retail and Food & Beverage
Tourism
Private-Healthcare
Enterprise-Level
Firm-level intervention is imperative to address specific productivity constraints at the firm level and to ensure the achievement of industry and national productivity targets. This chapter will present the firm-level intenvention that will be undertaken in a systematic and structured manner, based on a diagnostic toolkit and using existing R&D intermediaries.